Zen 5 architecture and specification
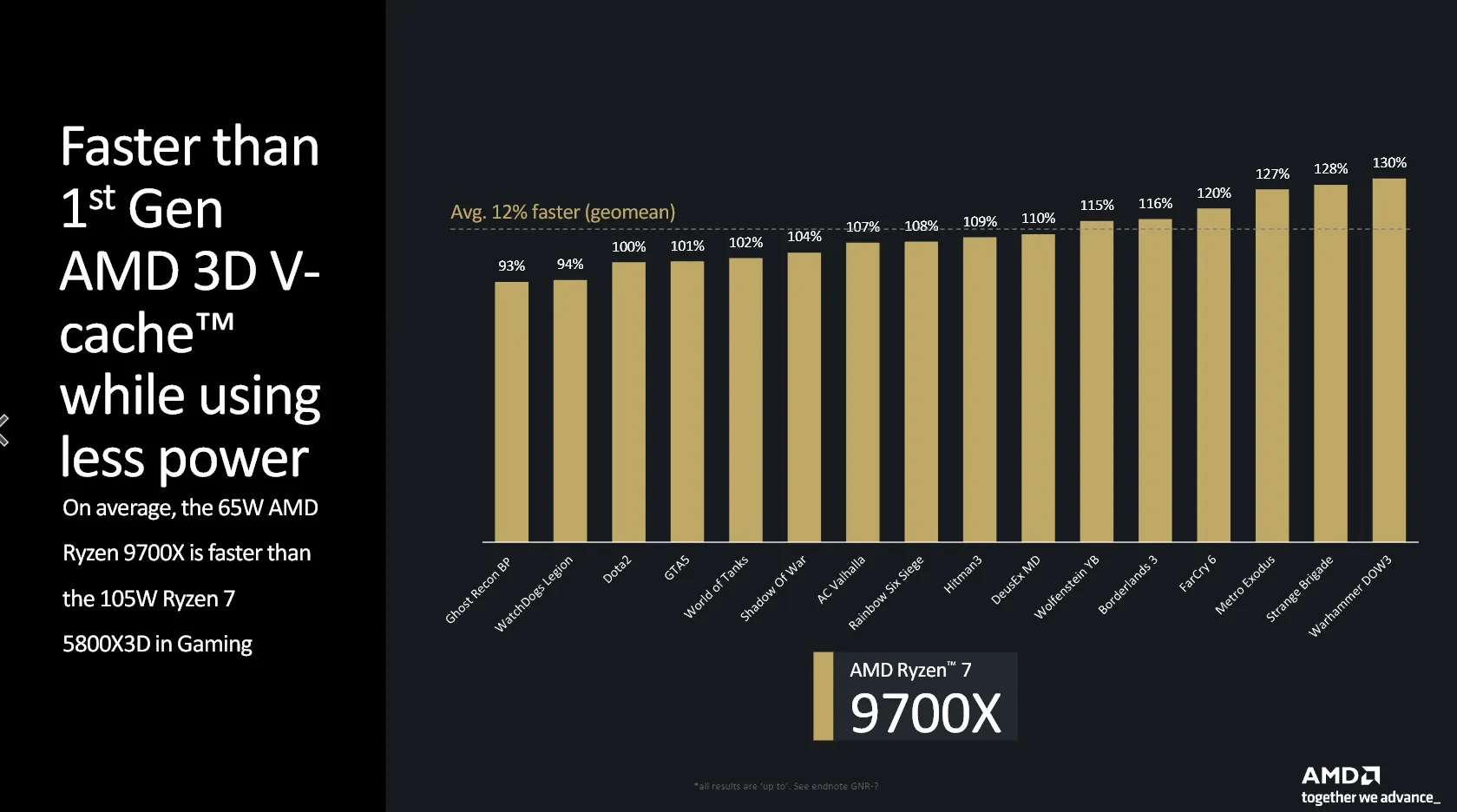
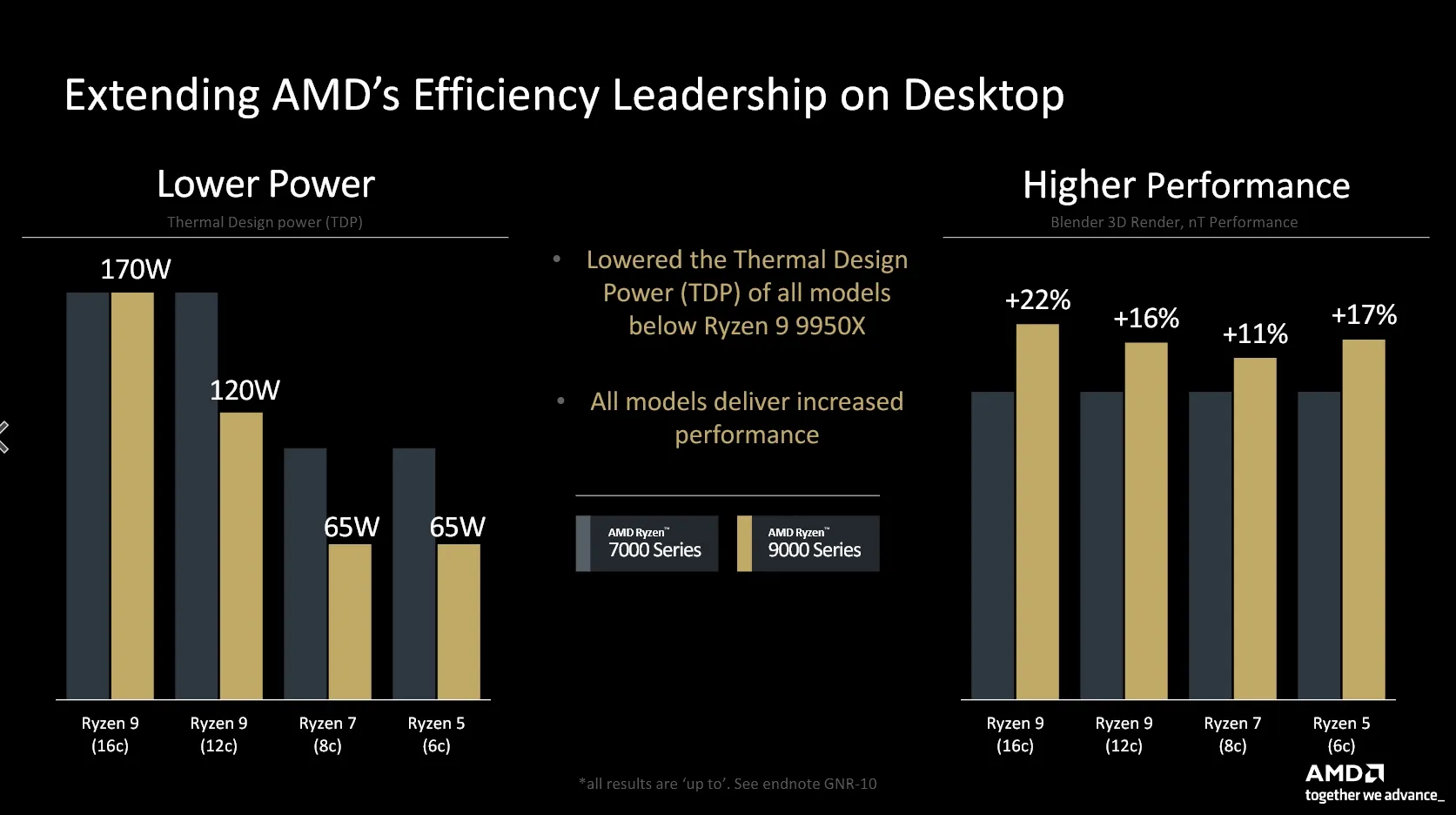
The Ryzen 7 9700X is noted to outperform the first-generation X3D SKU, the Ryzen 7 5800X, with an average performance increase of 12%. This claim is supported by a slide from AMD comparing the two models. However, it is also acknowledged that the Ryzen 7 9700X may not match the gaming performance of the Ryzen 7 7800X3D, based on statements from AMD’s Don Waligroski. AMD's launch presentation includes a series-to-series comparison, demonstrating an 11% to 22% performance improvement from the previous generation while simultaneously lowering the TDP for three of the four new SKUs. This reflects AMD's ongoing commitment to enhancing performance efficiency in their processor lineup. The Zen 5 architecture marks a significant advancement in AMD's Ryzen 9000 series processors for desktops. The structural aspects such as the socket and the internal layout remain consistent, featuring an unchanged I/O die and one or two CPU core dies, also compatible with the current series motherboards. AMD now also confirmed that these processors will be available starting July 31.
AMD Ryzen 9000 Series Overview
| Processor | Architecture | Cores/Threads | Boost Clock | Cache (L2+L3) | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 9 9950X | Zen 5 (TSMC 4nm) | 16C/32T | Up to 5.7GHz | 80MB | 170W |
| Ryzen 9 9900X | Zen 5 (TSMC 4nm) | 12C/24T | Up to 5.6GHz | 76MB | 120W |
| Ryzen 7 9700X | Zen 5 (TSMC 4nm) | 8C/16T | Up to 5.5GHz | 40MB | 65W |
| Ryzen 5 9600X | Zen 5 (TSMC 4nm) | 6C/12T | Up to 5.4GHz | 38MB | 65W |
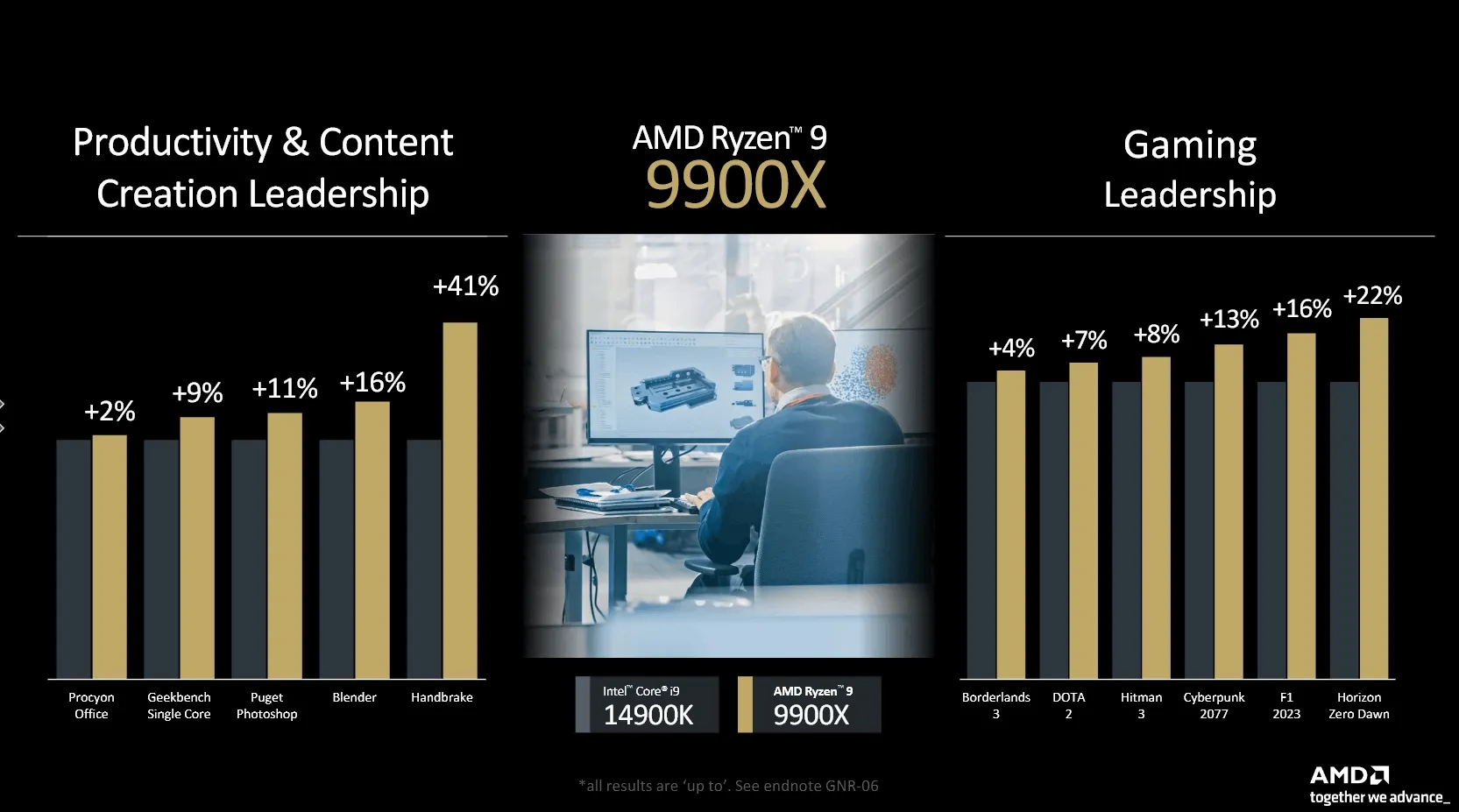
AMD has provided detailed performance benchmarks for the new AM5 CPUs, comparing them against Intel's 14th-generation Core processors. Notably, AMD's comparisons focus on productivity and content creation tasks as well as gaming performance. The 12-core Ryzen 9 9900X is highlighted against Intel's Core i9 14900K. In productivity and content creation tasks, the Ryzen 9 9900X shows performance improvements ranging from 2% to ~40%, with a notable 41% improvement in Handbrake due to the new AVX512 instructions in Zen 5. Other tasks like Photoshop and Blender see improvements of 11% and 16%, respectively. In gaming, the Ryzen 9 9900X outperforms the Core i9 14900K by 4% in Borderlands 3 and by 22% in Horizon Zero Dawn.
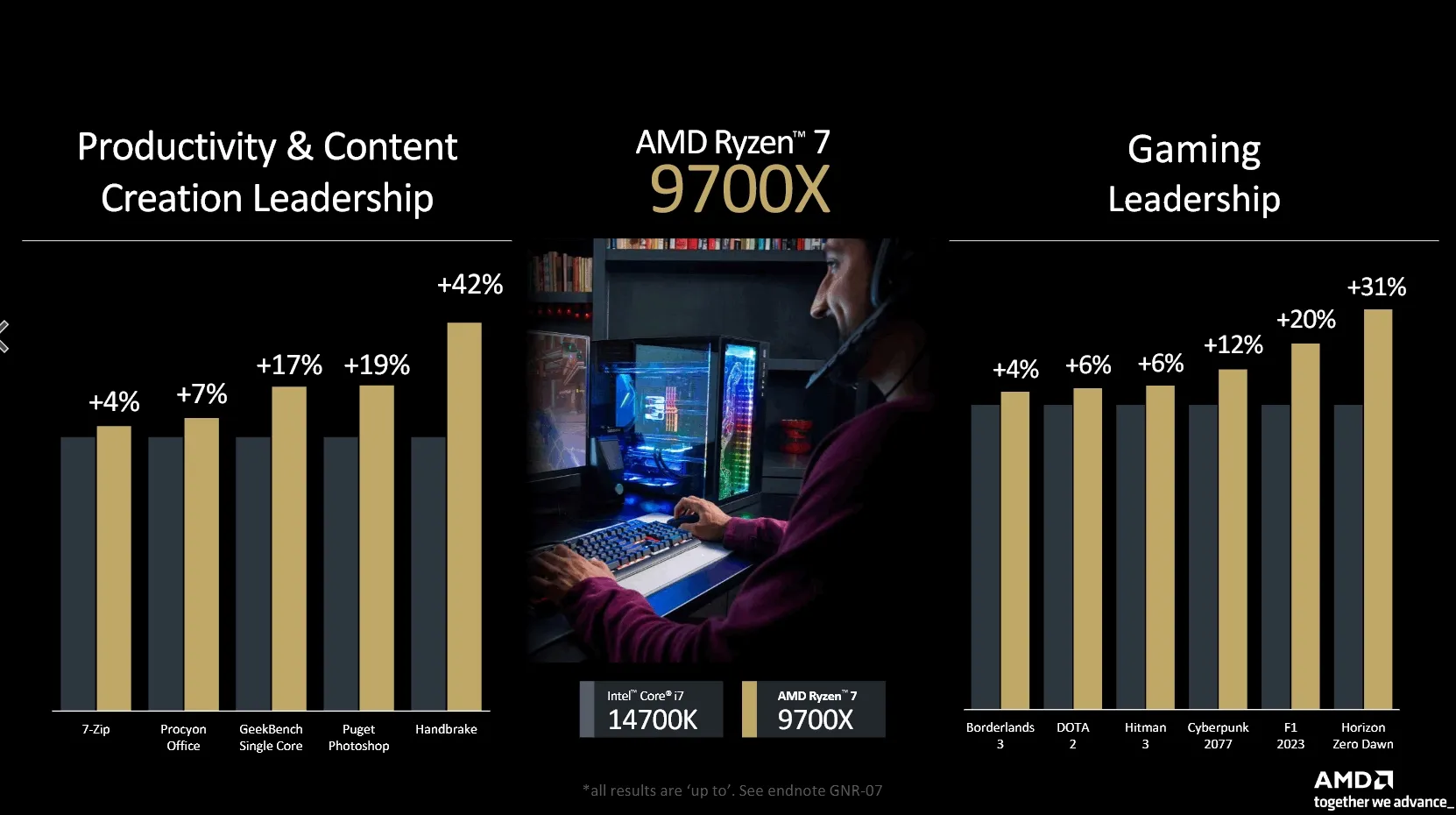
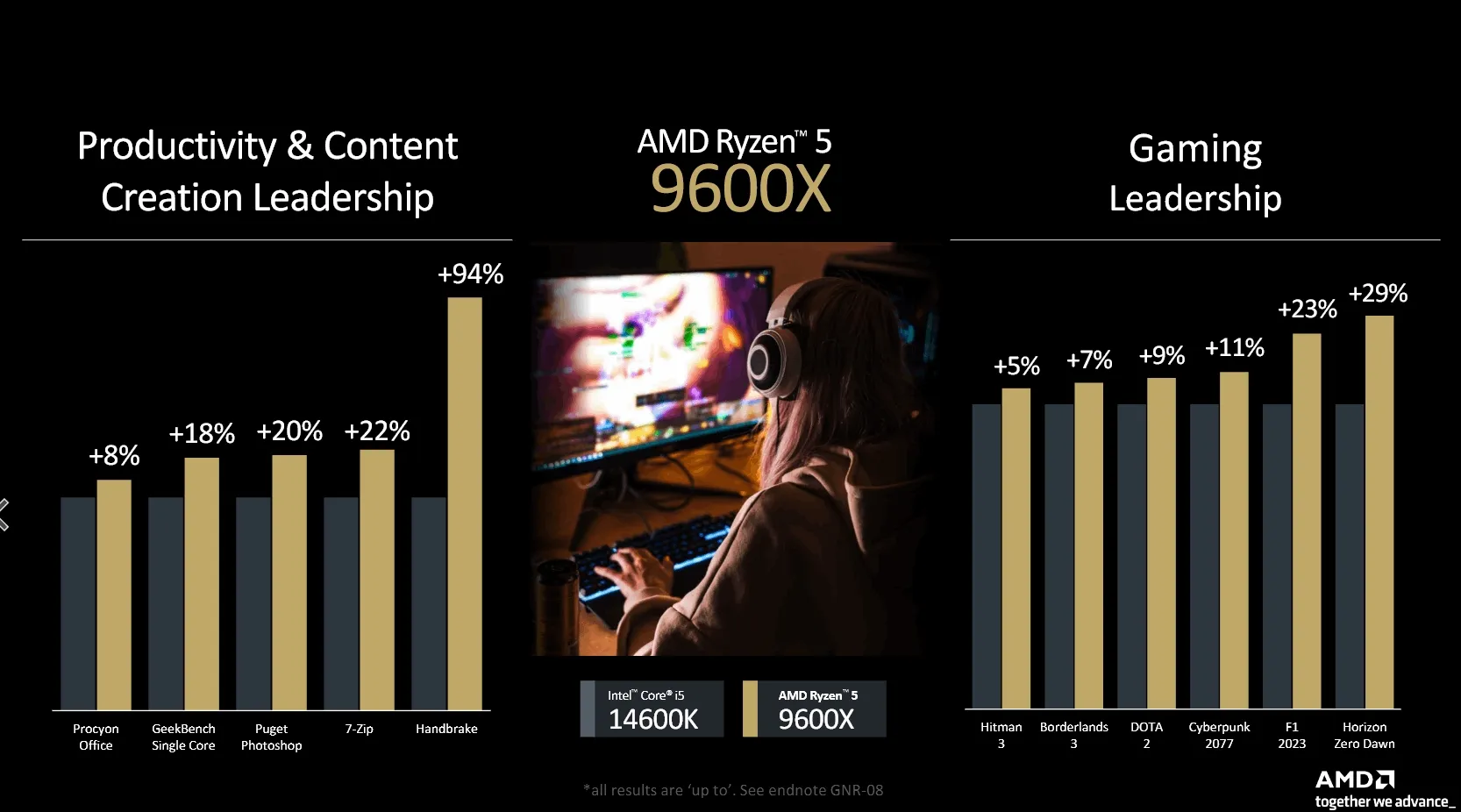
For the mid-range and lower-end models, the performance differences are even more pronounced. The 8-core Ryzen 7 9700X outperforms Intel's Core i7 14700K by 4% to 42% in productivity tasks and by 4% to 31% in gaming. The 6-core Ryzen 5 9600X demonstrates significant gains over the Core i5 14600K, with productivity performance improvements ranging from 8% to 94% and gaming performance gains between 5% and 29%. These benchmarks highlight the Zen 5 architecture's efficiency and its capability to leverage advanced instruction sets like AVX512, which contributes to higher performance in certain applications. AMD's strategic choice to compare the Ryzen 9 9900X against Intel's Core i9 14900K, rather than the top-tier Ryzen 9 9950X, indicates a confident positioning of their processors within the market segments.
Technical Overview and Market Position
The Ryzen 9000 series processors utilize TSMC's 4nm process technology, enabling high core counts and elevated boost clocks while maintaining manageable power consumption. The Ryzen 9 9950X, with 16 cores and a 5.7GHz boost clock, represents the pinnacle of the lineup, targeting high-end desktop users who require substantial processing power for demanding applications. The consistent socket and layout ensure compatibility with existing AM5 infrastructure, facilitating upgrades for current users. The inclusion of substantial L2 and L3 cache across the lineup enhances performance, particularly in data-intensive tasks. The announced AMD Ryzen 9000 series contains four (initial) models, all of which feature lower Thermal Design Power (TDP) ratings compared to the Ryzen 7000 series. Notably, only the Ryzen 9 9950X maintains the same 170W TDP as its predecessor. The 12-core Ryzen 9 9900X reduces its TDP from 170W to 120W, while the 6-core and 8-core models see a reduction from 105W to 65W.
Despite the lower power consumption, the new Ryzen 9000 models demonstrate improved performance. For example, the Ryzen 9 9700X, when compared to the Ryzen 7 5800X3D for socket AM4, shows an average performance increase of 12% across sixteen games, while consuming less power. This signifies that AMD has effectively surpassed the performance gains provided by 3D V-Cache technology within two years through advancements in architecture, clock speeds, and efficiency.
Lower Temperatures
The Ryzen 9000 series CPUs are also designed to operate at lower temperatures than their predecessors. The previous generation CPUs, even with efficient cooling solutions, often exceeded 90 degrees Celsius under moderate load. The new series addresses heat production more effectively by optimizing the chip layout and enhancing the placement of temperature sensors, which reduces thermal resistance by 15%. Consequently, this results in a 7 degrees Celsius reduction in operating temperature at the same power consumption levels.
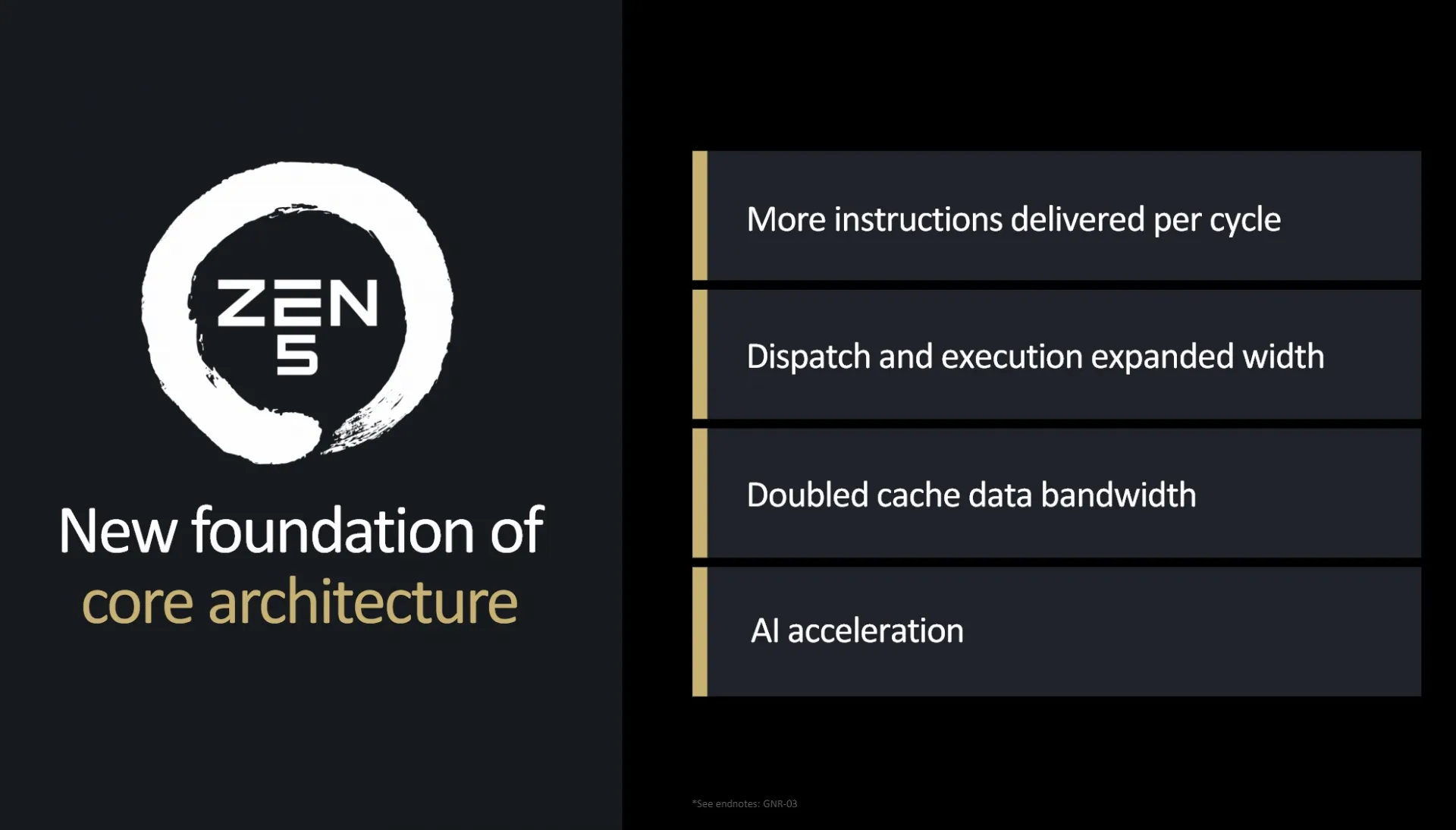
Zen 5 Architecture
AMD staff has detailed the enhancements introduced in the Zen 5 architecture. What initially appears as a minor update actually includes significant revisions that set the stage for future generations of AMD processors. Despite Intel's decision to discontinue Simultaneous Multi-Threading (SMT) in their P-Cores with the upcoming Lunar Lake and Arrow Lake architectures, AMD reaffirms the importance of SMT in their processors. AMD's implementation of SMT continues to be a core feature, offering substantial performance improvements with minimal additional space usage—typically 5 to 10 percent increase in die area resulting in 20 to 50 percent performance gains. While SMT may not benefit every application, it remains crucial for achieving optimal performance, providing better performance per dollar spent.
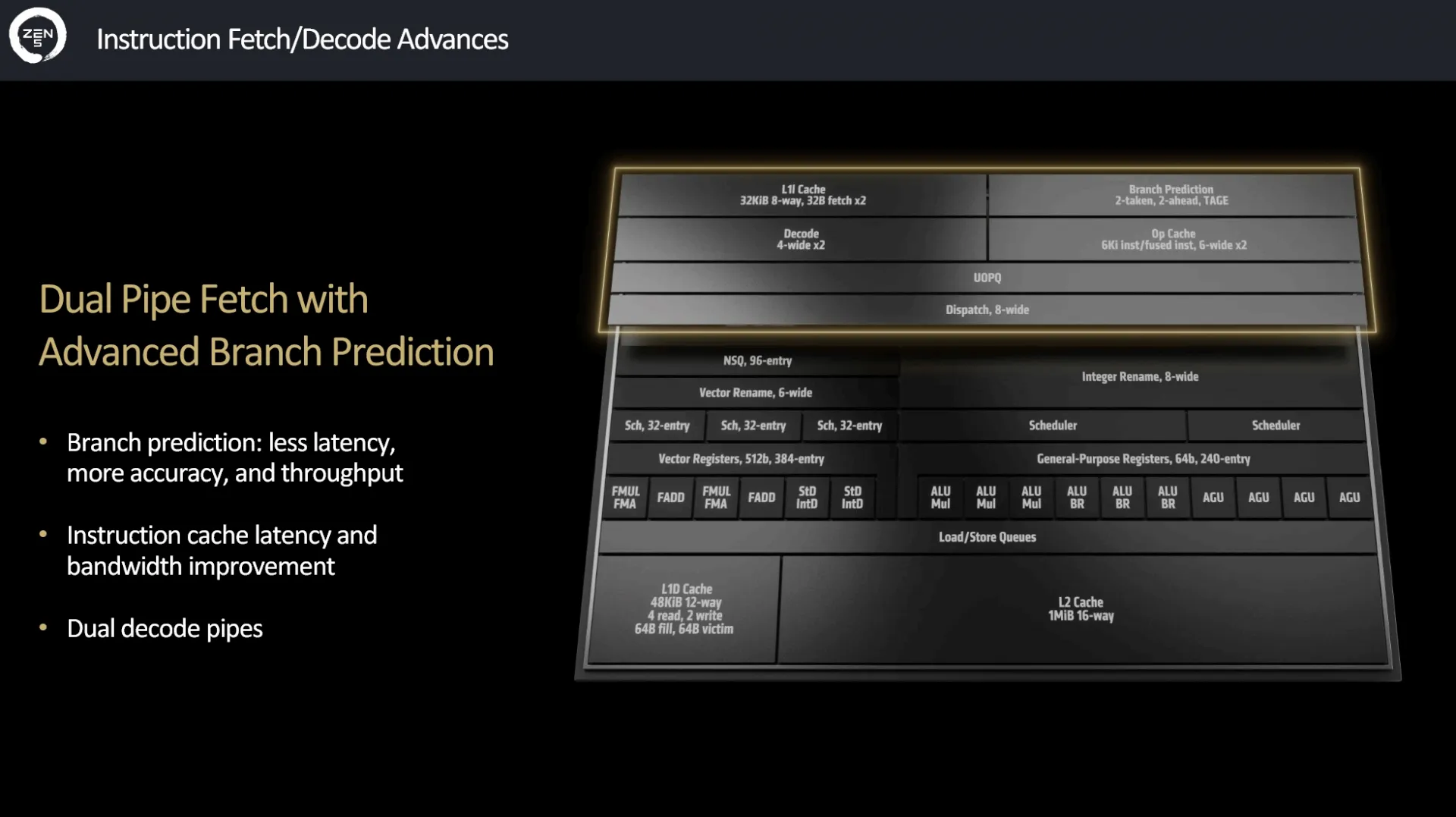
Enriched Front-End Capabilities
Zen 5 introduces a dual decoder path in the front end, alongside improved TAGE branch prediction. This branch prediction is more accurate, reliable, and operates with low latency, processing more predictions per cycle. To handle the increased predictions, a dual port has been integrated into the micro-op cache and decoder. This results in higher performance compared to Zen 4, with more instructions per clock delivered to the back end through a wider interface. The back end of Zen 5 now features an optimized dispatch mechanism that is eight instructions wide, allowing for the processing of more commands simultaneously. Unified schedulers contribute to this enhanced throughput. Additionally, the "execution window" has been expanded by 40 percent to accommodate 448 instructions, maintaining high performance and energy efficiency. The L2 cache has been increased by 50 percent to 48 KB, without compromising latency, which remains at 4 loads per cycle. This improvement supports higher data transfer rates, crucial for the new AVX-512 unit. The 512-bit AI Datapath benefits from doubled bandwidth from both the L1 and L2 caches. The AVX-512 unit, now operating at a full clock speed of 5.7 GHz, enhances performance in areas such as gaming, high-performance computing (HPC), and content creation. It also supports splitting into two 256-bit paths, providing flexibility depending on the application requirements. The Floating Point ADD (FADD) operation has been optimized to complete in 2 cycles instead of 3, further boosting the Floating Point Unit (FPU) performance.
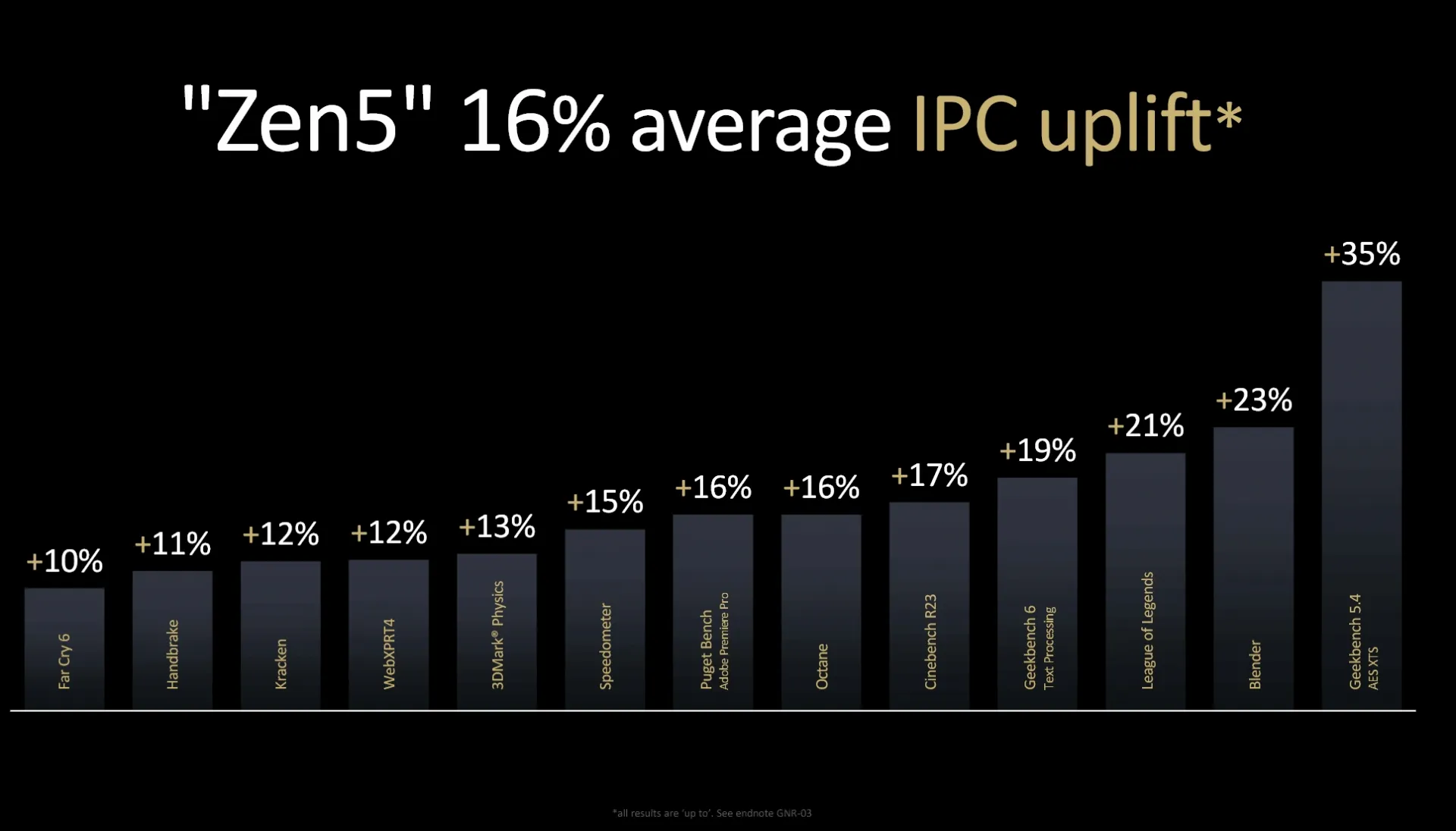
Significant IPC Gains
The cumulative effect of these optimizations and expansions results in a 16 percent increase in instructions per clock (IPC). The broader execution pipeline contributes 34 percent to this performance gain, with the decoder and op cache improvements accounting for 27 percent each. Enhanced bandwidth further adds to this growth. Specific benchmarks, such as Geekbench's AES-XTS test, showcase a 35 percent increase in single-core performance at the same clock speed, pushing overall Geekbench scores higher. Browser-based applications exhibit around 12 percent IPC growth compared to Zen 4, demonstrating widespread improvements across different workloads.
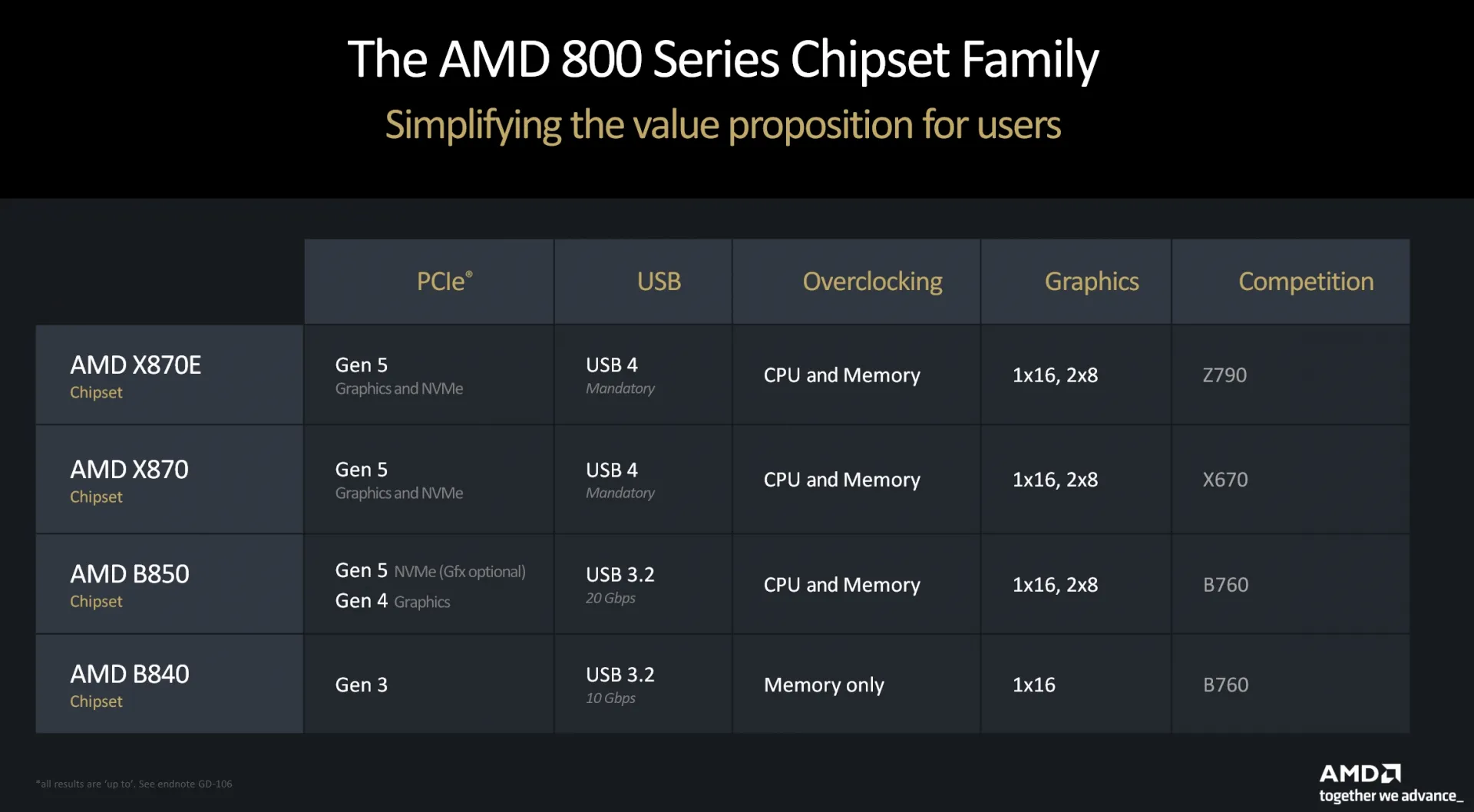
2nd Generation AM5 Platform with X870E and X870 Chipsets
AMD has announced the launch of its 2nd Generation AM5 platform, introducing the new 800-series chipsets, beginning with the high-end X870E and X870 motherboards. This release will be followed by more mainstream options. The AMD AM4 platform, initially introduced in 2017, continues to be relevant in 2024, with recent chip releases extending its viability until 2025. However, AMD is now shifting focus to its new AM5 platform, specifically the 800-series family aimed at enthusiasts. The X870E and X870 chipsets are designed to deliver enhanced features, improved I/O memory support, and additional overclocking capabilities for current and future Ryzen CPUs, including the Zen 5-based Ryzen 9000 "Granite Ridge" family. Several significant upgrades have been made in the AMD X870E and X870 motherboards:
- USB 4.0 Standard: All X870 and X870E motherboards come equipped with USB 4.0 support.
- PCIe Gen5: These motherboards support PCIe Gen5 for both graphics and NVMe storage.
- Higher EXPO Memory Clock Support: Enhanced memory clock speeds are supported on all X870 and X870E motherboards.
AMD has also disclosed the introduction of new Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) and Curve Optimizer (CO) algorithms with Ryzen 9000 CPUs, which will be fully supported by these new motherboards. In addition to the X870E and X870 motherboards, AMD plans to release the B850 and B840 chipsets targeting the mainstream market. The chipset lineup includes:
These motherboards will natively support DDR5-5600 MT/s memory speeds, with potential transfer rates exceeding 8000 MT/s on some high-end models, expected to be available by July.
AMD Ryzen 9000 Series Memory Overclocking and Curve Shaper Enhancements
This latest generation of AMD processors allows users to reach memory speeds as high as DDR5-8000 by implementing a 1:2 ratio between the memory controller speed and the memory speed itself. This represents an upgrade from the DDR5-5200 support in the Ryzen 7000 series to DDR5-5600, aligning with the memory speeds supported by Intel’s current processors. AMD has introduced a convenient tool for dynamic memory overclocking within Windows through its Ryzen Master software. This software includes a unique feature with a simple button that toggles between two pre-trained memory profiles. One profile adheres to the Jedec standard, ensuring stability for critical tasks, while the other, known as the EXPO profile, is tailored for optimal gaming performance.
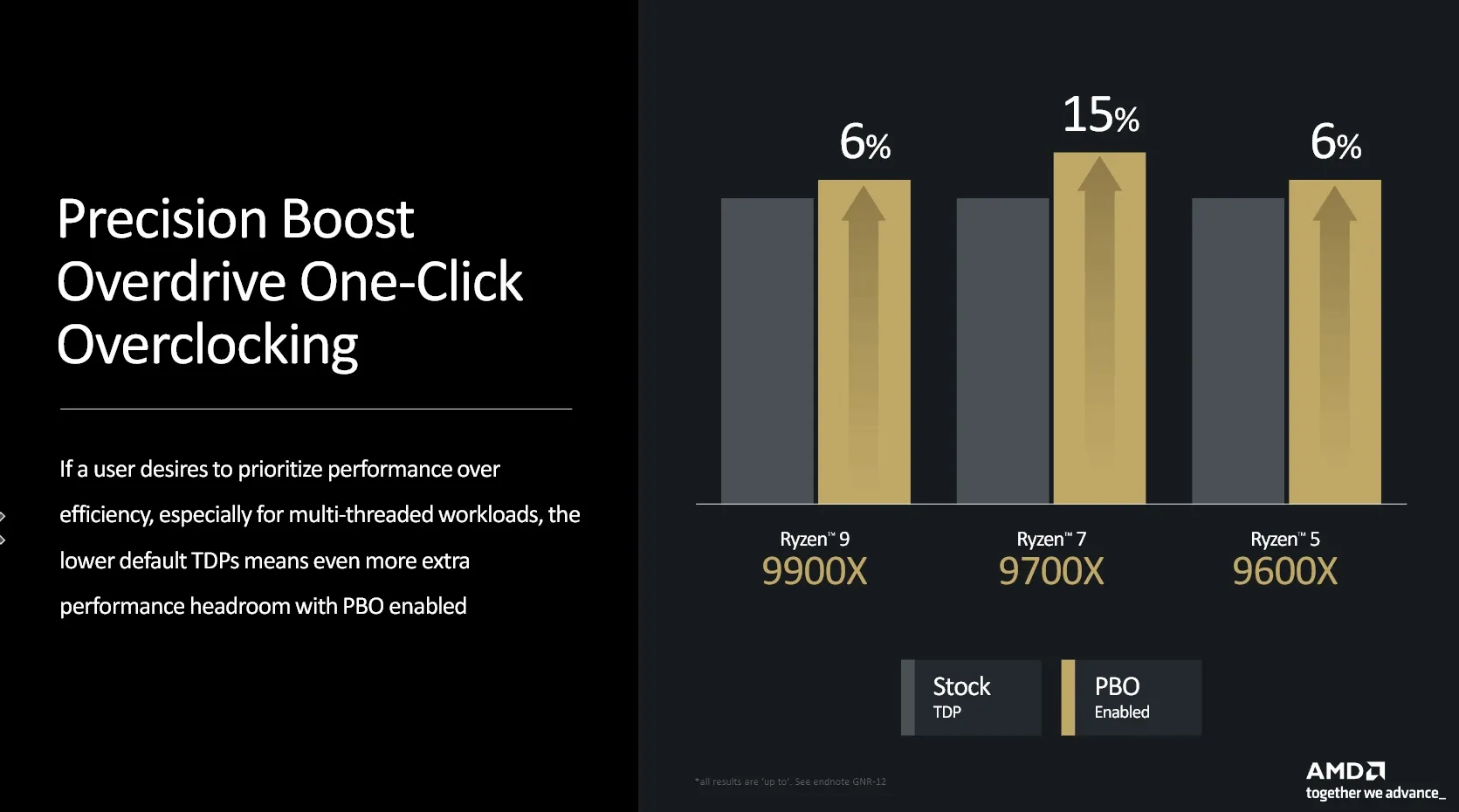
In addition to memory tuning, AMD has rolled out Curve Shaper, a novel feature accessible via the BIOS on AM5 motherboards compatible with Ryzen 9000 CPUs. Building on the existing Curve Optimizer, Curve Shaper enhances the ability to fine-tune processor performance. It does this by allowing adjustments to the voltage-frequency curve, enabling users to set specific undervolt offsets for different combinations of clock speeds and temperatures. This capability is designed to reduce power consumption, which in turn gives AMD’s Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) technology more flexibility to boost clock speeds and improve overall system performance.
The Ryzen 9000 CPUs also benefit from a lower thermal design power (TDP), which facilitates more significant performance improvements when using PBO compared to previous models. For instance, activating PBO on the 9600X or 9900X models can result in up to a ~5% increase in performance, while the 9700X might see a performance boost of up to 15%. However, the high-end 9950X model, which already operates at the peak allowable TDP, does not officially support PBO. Despite this, advanced users still have the option to manually raise power limits to squeeze out additional performance.
Preliminary conclusion
All in all the Granite Ridge series, Ryzen 9000 for desktops, marks a significant step forward from the previous Ryzen 7000 series. This new lineup boasts improvements like faster processing speeds, better energy efficiency, and enhanced overall performance due to an optimized design and an increased frequency range. These upgrades make the Ryzen 9000 series a strong competitor in the computer processor (CPU) market. One of the standout features of the Ryzen 9000 series is its enhanced efficiency. These CPUs manage energy better, which means they use less power while delivering higher performance. This improvement is vital in both everyday and professional settings where getting the most out of each watt of power is important. The top models of the Ryzen 9000 series benefit greatly from these design improvements, achieving higher speeds that significantly boost performance compared to earlier models. The release of the Ryzen 9000 series comes at a strategic time and could affect Intel's position in the market, especially considering some challenges Intel faces with its K series CPUs. With Intel's new Arrow Lake processors delayed until October, AMD has a chance to capture more of the market. Intel's existing Core series also faces performance issues, which could lead more consumers to choose the newer and more efficient Ryzen 9000 series. A thorough review and benchmark testing of the Ryzen 9000 series will be necessary to confirm these performance benefits. The official launch is set for July 31st, a key date when AMD will announce final prices and detailed specifications.